|
Inhaltsübersicht | Nanomaschinen | Moleküle | Programme | Kurse | Fun | Links |
||
| > |
Carotenoid Oxygenase
Carotenoid Oxygenase
Eat your carrots or you'll go blind! The biochemical reason for this childhood warning is that we need retinal, vitamin A, to form the pigment that absorbs light in our eyes. Unfortunately, our cells cannot make it for themselves, so we have to obtain it in our diet. We typically get our daily dose of vitamin A in two different ways. Retinal, or molecules similar to it, may be obtained directly when we eat meat. Alternatively, we can eat molecules that are easily transformed into retinal. This is where the carrots enter the story. They are full of beta-carotene, which our cells break in half to form two molecules of retinal.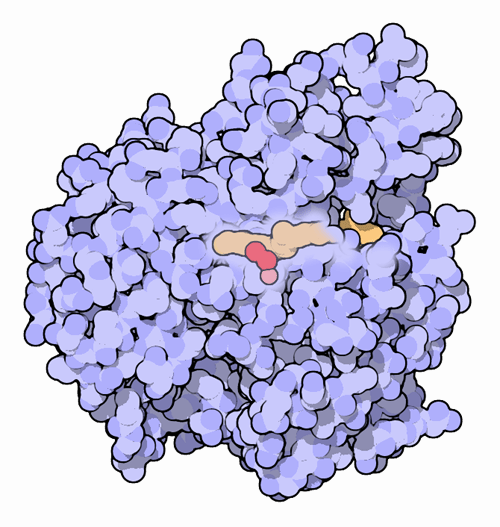
Colorful Carotenoids
The bright color of carrots and many other orange and yellow vegetables is caused by carotenoid molecules such as beta-carotene. Carotenoids are long, thin molecules with a string of carbon-carbon double bonds in a row. These bonds absorb light and give carotenoids their characteristic yellow color. Hundreds of different types have been discovered in different plants, where they color flowers, leaves, fruits, and even the roots. Carotenoids are remarkably useful, both for the plant and for the people eating the plant. In plants, carotenoids assist the chlorophyll molecules that absorb light in photosynthesis. Carotenoids also absorb excess light when it reaches dangerous levels. Our retinas contain carotenoids such as lutein that protect us from excess light that might damage our eyes. Carotenoids also are antioxidants that scavenge reactive forms of oxygen, destroying them before they damage our molecular machinery.Carotenoids in Pieces
Carotenoids provide the starting material for construction of many useful compounds. In plants, carotenoids are broken into small pieces that act as hormones and also form small, volatile compounds with pleasing floral scents. In your cells, you break carotenoids into vitamin A, or retinal, which is used to build visual pigments and is also used as a signaling molecule to control growth and specialization of cells in our tissues. Many of these breakage reactions are performed by carotenoid oxygenases, enzymes that use a molecule of oxygen to perform the cut.Cutting Carotenoids
Carotenoid oxygenases trap a carotenoid molecule inside a deep pocket and break it into two pieces using oxygen. An iron ion assists in the reaction, positioning the oxygen at the proper place and activating it. The enzyme shown here, from PDB entry 2biw, is from a cyanobacterium. It breaks a variety of carotenoids at a bond at the center. Our own enzyme breaks beta-carotene in the center, forming two molecules of retinal. For more information on this family of enzymes from a genomic perspective, visit the Protein of the Month at the European Bioinformatics Institute.Last changed by: A.Honegger,